sysinfo - get system-specific information
SYNOPSIS<sysinfo $what [$arg ...]>
DESCRIPTION
The sysinfo function obtains various system- or OS-level
parameters. This information can be used to monitor the performance
of large or long-running processes. The $what argument
determines what is returned:
-
time -
time wallclock -
time continuousfixedrate[orwallclock] -
time continuousvariablerateGiven second arg
wallclock(or empty/no second arg), returns the current wall-clock (real) time, in seconds since midnight Jan. 1 1970 GMT, as a double. Fractions of a second up to the system clock resolution are returned as well. This is the same value as Unix date displays, but with sub-second resolution. It can be printed and inserted as a Texisdatevalue. Note: User and system time - obtainable with theproctimeoption - more accurately reflect the CPU utilization of a process. Also, the time needed to fetch a Web page is obtainable with options tourlinfo(here).Given second arg
continuousfixedrate, the time from a fixed-rate, continuous clock is returned, as adoublevalue of seconds (plus fraction). This clock continuously increments at a fixed rate; the starting point and rate are fixed at boot. Thus it is not affected by forward/backward jumps in the system time (e.g. when the Unix date is set), nor by rate changes in the system time (e.g. from NTP speedup/slowdown). However, this clock's epoch (zero starting point) is undefined; it is not midnight Jan. 1 1970 GMT, so printing it as a Texisdatevalue will give meaningless year/month/day/etc. values. It should only be used for comparison with othercontinuousfixedratetimes during the same system lifetime (i.e. since boot). It can be used to set deadlines or time events in a manner that is unaffected by system time changes. On platforms where this clock is unsupported, -1 is returned. To avoid a -1 return, the second arg may be given ascontinuousfixedrateorwallclockinstead, which returns a continous fixed-rate clock time if supported, or the ordinary wall-clock time if not; this option was added in version 7.07.1568044000 20190909.Given second arg
continuousvariablerate, a clock similar tocontinuousfixedrateis returned, except that the rate may vary. I.e. it is subject to the same speedup/slowdown as the system clock, but not the system clock's jumps; this clock will continuously increment, regardless of date changes. On platforms where this clock is unsupported, -1 is returned.The
wallclock,continuousfixedrateandcontinuousvariableratearguments were added in version 7.06.1510695000 20171114. -
boottimeReturns the system boot time, in seconds (plus fraction) since midnight Jan. 1 1970 GMT. Added in version 7.06.1510695000 20171114.
-
proctimeReturns user, system and real process times, in seconds since process start, as 3 double values. These are the number of seconds the process has spent actually running (user), doing system calls (system), and wall-clock time since process start (real). If the optional$argargument is given, those values are first subtracted. This allows a certain section of the process to be measured, instead of the entire cumulative process time (see example below). On error, values of -1 are returned. -
procmemReturns virtual size and resident set size of the process, in bytes, as 2
longorint64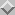 values. On error, or
if the current OS is unsupported, values of -1 are returned.
Although the exact definition varies by platform, the virtual size
is typically the total memory used by the process (code, data and
stack), and the resident set size is the amount of that memory
currently in physical RAM (as opposed to disk swap).
values. On error, or
if the current OS is unsupported, values of -1 are returned.
Although the exact definition varies by platform, the virtual size
is typically the total memory used by the process (code, data and
stack), and the resident set size is the amount of that memory
currently in physical RAM (as opposed to disk swap). -
physmemReturns the amount of physical memory the system contains, in bytes, as a
longorint64value. If this cannot be determined, -1 is returned. Added in version 3.01.981000000 20010131. -
getpidorpidReturns the process ID, as an integer. Same as thegetpidfunction (here). -
getppidorppidReturns the parent process' ID, as an integer. Not supported for Windows. -
procexistsFor each process ID given in the$arglist, returns 1 if that process exists, 0 if not. Same as theprocexistsfunction (here). -
loadavgReturns the 3 system load averages as doubles, or -1 if unavailable or the OS is unsupported. Same as theloadavgfunction (here). -
cwdorpwdorgetcwdReturns the current working directory of the process. -
cputimes[$cpu]$timeNameReturns the (system-wide) CPU time(s), asdoubleseconds, for the selected CPU(s) for time$timeName, which is one of the following values (from Linux /proc/stat cpu values):-
user -
nice(Linux only) -
system(under Windows, kernel time - which includes some idle time) -
idle -
iowait(Linux 2.5.41+ only) -
irq(Linux 2.6.0+ only) -
softirq(Linux 2.6+ only) -
steal(Linux 2.6.11+ only) -
guest(Linux 2.6.24+ only) -
guestnice(Linux 2.6.33+ only)
$cpuargument is one ofsum(the default),all,cpuN or N.sumreturns a single summary value across all CPUs.allreturns an array with a value for each CPU.cpuN or N returns a single value for the integral Nth CPU, 0-base indexed.-1.0 value(s) are returned on error. Unknown
$cpu/$timeNamevalues also report a putmsg. Values that are known but unsupported on the current machine (platform-dependent - see notes above - or out-of-range CPU) silently return -1.0 (potentially multiple times if CPUallrequested).Added in version 8.01.1707413956 20240208.
-
-
platformReturns a string describing the hardware, vendor, OS and file bit size that this executable was created for, and is probably running on. Returned as 4 values separated by dashes. Added in version 3.01.980200000 20010122. Note that this may vary from the actual platform that is running, e.g. the revision of the OS. -
regquery$key$subkey$name[$default]Under Windows, queries the registry under the given$keyand$subkeyfor the value associated with$name.$keymust be one of the predefinedHKEY_... values such as "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE".$subkeyis generally a string "path". If there is no value defined, the$defaultvalue is returned if given. Under non-Windows platforms this function is unimplemented; the$defaultvalue is always returned. Added in version 3.01.976300000 20001208.regqueryvalueis an alias forregquery. -
resourcestat[$who]$statNameReturns the current process's usage of the resource named by$statName, which is one of the following:-
UserTime -
SystemTime -
RealTime -
MaxResidentSetSize -
IntegralSharedMemSize -
IntegralUnsharedDataSize -
IntegralUnsharedStackSize -
MinorPageFaults -
MajorPageFaults -
Swaps -
BlockInputOps -
BlockOutputOps -
MessagesSent -
MessagesReceived -
SignalsReceived -
VoluntaryContextSwitches -
InvoluntaryContextSwitches
$whoparameter is one ofself,children,bothorthread; the default isself. This determines which resource group the value is returned from. Not all platforms support all resources, nor all$whovalues. Added in version 7.01.1384824000 20131118. -
-
umaskReturns the process's umask, as achmod-style symbolic string. Added in version 4.00.997400000 20010809. -
getenv $varReturns the value of environment variable named by$var. Note: Vortex variables are automatically initialized from environment variables; e.g.$PATHin Vortex contains the path from the environment. This call is less efficient, and should only be needed if environment variables have been changed since script start withsyscp setenv. Added in version 4.00.997400000 20010809. -
availablespace $pathReturns the amount of free disk space in bytes (for non-
rootusers) for each filesystem in$path, as anint64value. If the free space cannot be determined, -1 is returned. On some old platforms an inaccurate value may be returned. Added in version 7.05.1450200000 20151215. -
freespace $pathReturns the amount of free disk space in bytes (for
root) for each filesystem in$path, as anint64value. If the free space cannot be determined, -1 is returned. On some old platforms an inaccurate value may be returned. Added in version 4.04.1080180000 20040324. In versions prior to 7.05.1450200000 20151215, this returned the same asavailablespace, i.e. space for non-rootusers. -
totalspace $pathReturns the total disk space in bytes for each filesystem in
$path, as anint64value. If the total space cannot be determined, -1 is returned. On some old platforms an inaccurate value may be returned. Added in version 7.05.1450200000 20151215. -
usedspacepercent $pathReturns the used disk space for each filesystem in
$path, as adoublepercent value. If the total space cannot be determined, -1 is returned. On some old platforms an inaccurate value may be returned. Added in version 7.05.1450200000 20151215. -
hostnameReturns the machine's hostname as configured. Added in version 4.04.1080000000 20040322. -
fullhostnameReturns the machine's hostname, fully-qualified via DNS if possible. Added in version 4.04.1080000000 20040322. -
userorrealuserReturns the real user name running the script. Added in version 4.04.1072150000 20031222. In version 7.00.1352762000 20121112 the alias
realuserwas added. In version 8.00.1634252269 20211014 and later the domain is included under Windows. -
effectiveuserReturns the effective user name running the script. Added in version 7.00.1352762000 20121112. In version 8.00.1634252269 20211014 and later the domain is included under Windows. -
maxdescriptorsReturns the maximum number of open file descriptors possible, or -1 if unknown. Added in version 4.02.1037476167 20021116. -
opendescriptorsReturns the current process's number of open file descriptors, or -1 if unknown. Added in version 4.02.1037476167 20021116. Windows support added in version 8.01.1711936048 20240331. -
processdescriptionReturns process description (sans "texis: " prefix) currently set by
<syscp processdescription>(here), or empty if none. Added in version 7.06.1522794000 20180403. Note that the returned description may be truncated from the value passed to<syscp processdescription>, due to limited original command line space in the process. -
maxprocessdescriptionlenReturns maximum length in characters of a process description that can be passed to<syscp processdescription>(here) without truncation. Added in version 7.06.1522794000 20180403.
DIAGNOSTICSsysinfo returns various OS-level parameters depending on
its first argument.
EXAMPLE
To obtain the CPU utilization of an entire script, call
<sysinfo proctime> at the end. In this example, we time a
single function call, <CPUhog>, while ignoring any previous
or later functions:
... ignore time of earlier calls here ...
<sysinfo proctime>
<$start = $ret>
<CPUhog>
<sysinfo proctime $start>
CPUhog times: <LOOP $ret> $ret </LOOP>
...
CAVEATS
The sysinfo function was added in version 3.01.967500000 20000828.
Some options may be unavailable on some platforms, or may require
additional user privileges (such as reading kernel memory). Vortex
should not be run as root to obtain these privileges; use
a lower privilege user that still has the required perms
(e.g. kmem). No databases should be accessed when running as
such a non-Texis user, to avoid making files inaccessible to
other (Texis user) invocations of Vortex.
Copyright © Thunderstone Software Last updated: Apr 15 2024